Author: Rashi Pareek | EQMint | Sustainability News
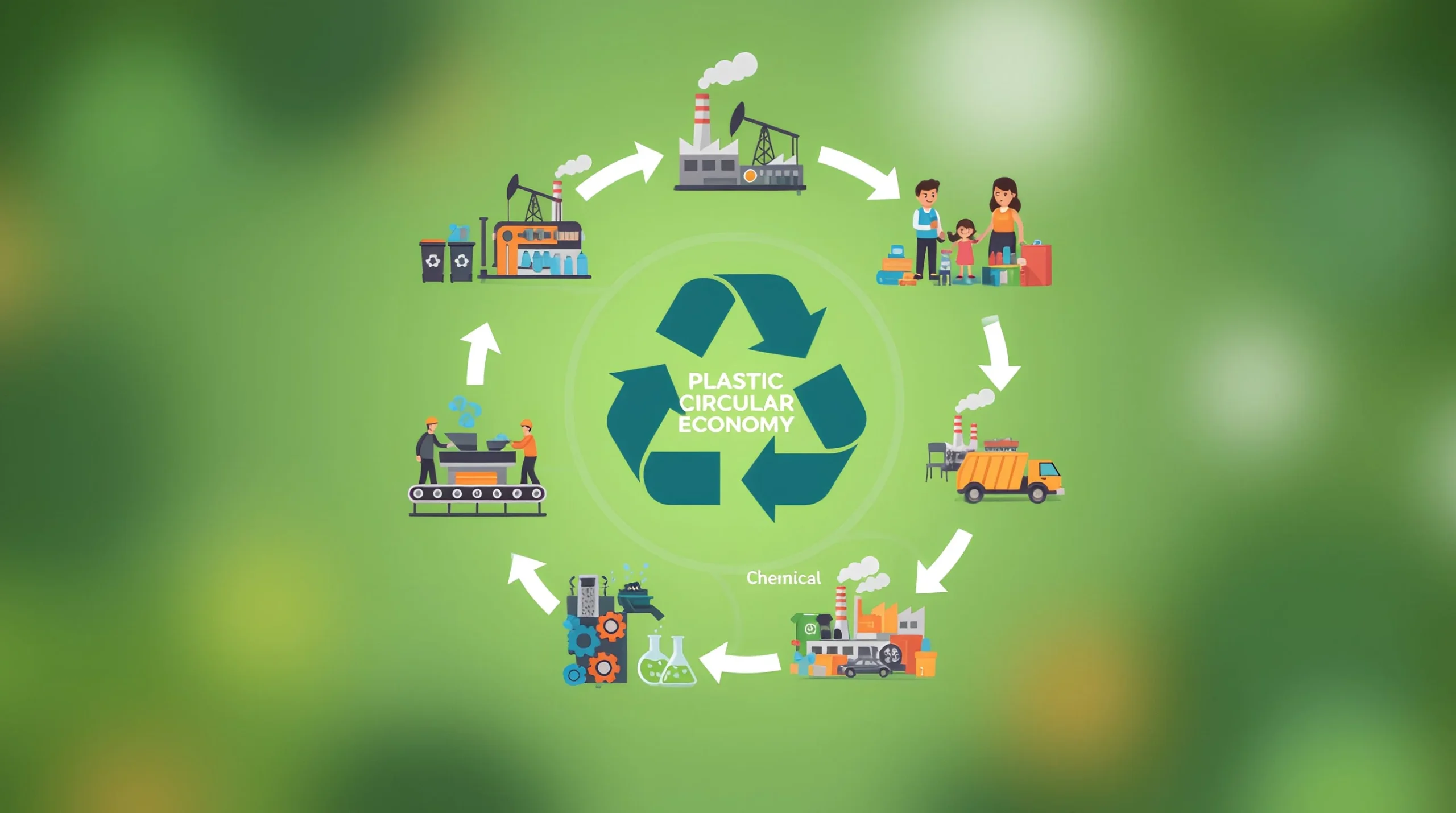
India’s plastic waste challenge has rapidly evolved from an environmental concern into a strategic business and investment opportunity. Rising plastic consumption, accelerating urbanisation, and tightening regulatory frameworks are transforming the recycling sector into a high-growth industry. For companies, investors, and emerging enterprises, this shift presents both a responsibility and a commercial pathway to build scalable circular models.
Market Scale and Growth Dynamics
India is among the world’s largest producers and consumers of plastic, generating over 9 million tonnes of plastic waste annually. Recent industry analyses estimate the Indian waste plastic recycling market at approximately 10.9 million tonnes in 2024, with projections exceeding 25 million tonnes by 2033 at a CAGR of around 9.4 percent.
Parallel market valuations place the plastic recycling sector at USD 2.18 billion in 2024, expected to grow at a CAGR of more than 10 percent through 2030. The data makes one point clear: plastic recycling is no longer peripheral. It is a rapidly expanding industrial segment influencing India’s manufacturing landscape and sustainability trajectory.
Key Business Drivers
1. Rising Corporate Demand for Recycled Plastics
Leading FMCG and packaging companies are integrating recycled plastics into their supply chains to meet sustainability commitments and manage material costs.
2. Strengthening Regulatory Mandates
India’s Plastic Waste Management Rules and Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) framework require producers and brand owners to collect and recycle a defined share of their plastic output. This is accelerating brand–recycler partnerships.
3. Technological Advancements
Innovations in sorting, washing, and extrusion are enabling production of higher-quality recycled resins, including food-grade materials, improving market acceptance.
4. Transition from Informal to Formal Systems
The gradual formalisation of India’s informal recycling network is enhancing traceability, compliance, and investor confidence.
5. Economic Competitiveness
With fluctuating crude oil prices and global sustainability pressure, recycled feedstock is emerging as a cost-efficient, resilient material choice.
Industry Challenges
Despite strong momentum, the sector faces structural constraints:
-
- Contaminated, mixed waste streams reduce overall feedstock quality.
-
- High capital requirements for producing food-grade and premium recycled resins.
-
- Price pressure due to volatility in virgin polymer markets.
-
- Increasing compliance burdens under EPR and CPCB standards.
-
- Integration of waste picker communities into formal, traceable systems.
Strategic Opportunities for Enterprises
Vertical Integration
Companies can secure long-term feedstock by partnering with waste aggregators or establishing material recovery facilities.
Collaborative Circular Models
Brand collaborations on bottle-to-bottle and other closed-loop recycling systems are becoming key differentiators.
Premium Materials
Investments in producing high-spec rPET and rHDPE open access to premium packaging and industrial applications.
EPR Credit Monetisation
Recyclers offering verified traceability and compliance documentation are positioned to unlock strong revenue streams.
Digital Traceability Platforms
Technology-driven tracking systems enhance transparency across collection, processing, and resale stages, increasing investor confidence and operational efficiency.
Spotlight: Plastics Recycling Show India 2025 (PRS India)
The Plastics Recycling Show India 2025, scheduled for 13–15 November at the Bombay Exhibition Center, represents a pivotal platform for stakeholders in the recycling and circularity ecosystem. The event convenes recyclers, technology suppliers, policymakers, and brand leaders to discuss trends shaping India’s plastic circularity landscape.
Key opportunities at PRS India 2025 include:
-
- Networking with recycling technology innovators and investors
-
- Insights into upcoming policy reforms
-
- Collaboration opportunities for sustainable packaging
-
- Exposure to advancements in chemical recycling and digital waste management
PRS India 2025 stands as a focal point for the next phase of India’s recycling transformation.
Leading Industry Players
Banyan Nation
Banyan Nation is recognised for its efforts in formalising the recycling value chain and producing high-quality rPE and rPP resins supported by proprietary traceability systems.
Gravita India Ltd.
Gravita operates across multiple recycling verticals, including metals, plastics, and batteries. Its expanding plastic recycling operations reflect India’s shift toward multi-material sustainability.
Ganesha Ecosphere Ltd.
One of India’s largest PET bottle recyclers, Ganesha Ecosphere converts post-consumer PET bottles into polyester fibre, yarn, flakes, and high-grade rPET. The company’s scale represents a successful model of turning waste into industrial value.
The Business Case for Recycling
For EQMint’s business, finance, and sustainability audience, plastic recycling offers measurable strategic advantages:
-
- Improved resilience against global raw material volatility
-
- Enhanced ESG and EPR compliance, attracting responsible capital
-
- Expansion into high-demand green materials markets
-
- Strong brand differentiation in sustainability-driven sectors
Conclusion
India’s plastic recycling industry stands at an inflection point. Consumer expectations, policy frameworks, and corporate commitments are propelling the sector from fragmented, informal operations to organised, technology-driven systems. As recycling integrates deeper into India’s industrial and manufacturing ecosystem, it presents significant opportunities for innovation, investment, and market leadership.
Events like PRS India 2025 reflect this transformation — moving the narrative from waste management to resource recovery. Businesses that invest early in circular infrastructure, strategic collaborations, and advanced technologies will not only meet compliance requirements but also help shape the future of sustainable industry in India.
For more such news and information visit EQMint.
Disclaimer: This article is based on information available from public sources. It has not been reported by EQMint journalists. EQMint has compiled and presented the content for informational purposes only and does not guarantee its accuracy or completeness. Readers are advised to verify details independently before relying on them.